DUODENAL ULCERS: These are erosions of the duodenal wall caused by the gastric juice that enters from the stomach. The most serious consequences are bleeding and perforation.
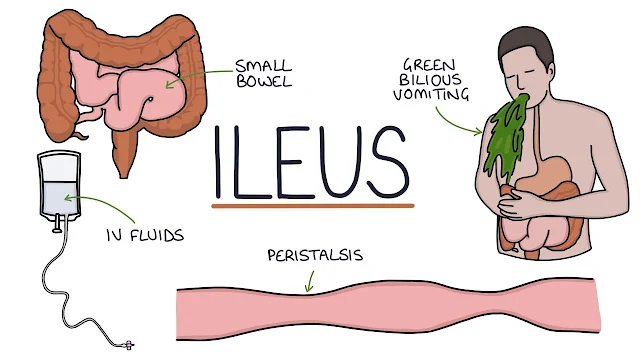
PARALYTIC ILEUS: This is the cessation of contraction of the smooth muscle layer of the intestine. This is a possible complication of abdominal surgery, but it may also be the result of peritonitis or inflammation elsewhere in the abdominal cavity. In the absence of peristalsis, intestinal obstruction may occur. Bowel movements cease, and vomiting occurs to relieve the pressure within the alimentary tube. Treatment involves suctioning the intestinal contents to eliminate any obstruction and to allow the intestine to regain its normal motility.
LACTOSE INTOLERANCE: This is the inability to digest lactose because of deficiency of the enzyme lactase. Lactase deficiency may be congenital, a consequence of prematurity, or acquired later in life. The delayed form is quite common among people of African or Asian ancestry, and in part is genetic. When lactose, or milk sugar, is not digested, it undergoes fermentation in the intestine. Symptoms include diarrhea, abdominal pain, bloating, and flatulence (gas formation).
SALMONELLA FOOD POISONING: This is caused by bacteria in the genus Salmonella. These are part of the intestinal flora of animals, and animal foods such as meat and eggs may be sources of infection. These bacteria are not normal for people, and they cause the intestines to secrete large amounts of fluid. Symptoms include diarrhea, abdominal cramps, and vomiting and usually last only a few days. For elderly or debilitated people, however, salmonella food poisoning may be very serious or even fatal.
DIVERTICULA: These are small outpouchings through weakened areas of the intestinal wall. They are more likely to occur in the colon than in the small intestine and may exist for years without causing any symptoms. The presence of diverticula is called diverticulosis. Inflammation of diverticula is called diverticulitis, which is usually the result of entrapment of feces and bacteria. Symptoms include abdominal pain and tenderness and fever. If uncomplicated, diverticulitis may be treated with antibiotics and modifications in diet. The most serious complication is perforation of diverticula, allowing fecal material into the abdominal cavity, causing peritonitis. A diet high in fiber is believed to be an important aspect of prevention, to provide bulk in the colon and prevent weakening of its wall.
RELATED;















No comments:
Post a Comment