INTRODUCTION: The plasma membrane separates the cell from the external environment and encapsules the microcellular organelles. It has highly selective permeability properties so that the entry and exit of compounds are regulated via specific protein-like channels also known as pores.
The cellular metabolism is in turn influenced and probably regulated by the membrane which is metabolically very active. The enzyme, nucleotide phosphatase or 5' nucleotidase and alkaline phosphatase are seen on the outer part of cell membrane; they are therefore called ecto-enzymes.
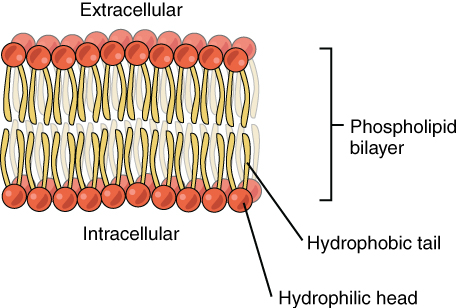
COMPONENTS OF THE MEMBRANE: Membranes are mainly made up of lipids, proteins and small amount of carbohydrates. The contents of these compounds vary according to the nature of the membrane. The carbohydrates are present as glycoproteins and glycolipids. Phospholipids are the most common lipids present and they are amphipathic in nature. Cell membranes also contain cholesterol.
FLUID MOSAIC MODEL: The lipid bilayer was originally proposed by Davson and Danielle in 1935. Later, the structure of the biomembranes was described as a fluid mosaic model. The phospholipids are arranged in bilayers with the polar head groups oriented towards the extracellular side and the cytoplasmic side with a hydrophobic core. The distribution of the phospholipids is such that choline containing phospholipids are mainly in the external layer and ethanolamine and serine containing phospholipids in the inner layer. The lipid bilayer shows free lateral movement of its components, hence the membrane is said to be fluid in nature. Fluidity enables the membrane to perform endocytosis and exocytosis. However, the components do not freely move from inner to outer layer, or outer to inner layer (flip-flop movement is restricted). During apoptosis (programmed cell death), flip-flop movement occurs. This Flip-flop movement is catalyzed by enzymes. Flippases catalyse the transfer of amino phospholipids across the membrane. Floppases catalyse the outward directed movement which is ATP dependent. This is mainly seen in the role of ABC proteins mediating the efflux of cholesterol and the extrusion of drugs from cells. The MDR (multi drug resistance) associated p-glycoprotein is a floppase.
The cholesterol content of the membrane alters the fluidity of the membrane. When cholesterol concentration increases, the membrane becomes less fluid on the outer surface, but more fluid in the hydrophobic core.
RELATED;
1. LIPIDS













No comments:
Post a Comment