INTRODUCTION: Retroviruses are unique in the sense that the flow of genetic information is reverse to the universal flow. In all other organisms, DNA is the store house of genetic information and from here it is transmitted to RNA. In retroviruses the sequence is RNA to DNA and consequent use of the enzyme reverse transcriptase. Genetic information is passed on from RNA to DNA through RNA-dependent DNA polymerase (reverse transcriptase).
INVASIVENESS OF RETROVIRUSES: The viral genetic information in DNA form is called as
provirus. This is capable of integration
into the host genome. On activation of
provirus, virus specific proteins are manufactured.
CLASSIFICATION:
The family Retroviridae comprised of three subfamilies: Oncovirinae,
Lentivirinae and Spumavirinae.
HUMAN T CELL LEUKAEMIA VIRUSES: The virion of human T cell leukaemia virus (HTLV) comprises icosahedral
core containing the RNA genome and surrounded by an envelope acquired as the
virion buds through the host cell membrane.
Virus specific envelope glycoproteins are inserted within the membrane
that surrounds the virus.
Antigens:
Three structural antigens are recognised in HTLV. These are core antigen, envelope antigen and
RT antigen. The RT or in full Reverse Transcriptase antigen is derived from a
polypeptide precursor which on being cleaved results into RT, protease and
endonuclease. RT is quite antigenic and
sera from infected patients contain antibody to it.
HUMAN IMMUNODEFICIENCY VIRUS: Emergence of this deadly disease appeared when the first
few cases of AIDS were detected in June, 1981 by the US. Centers for Diseases
Control and Prevention (CDC). They reported
a cluster of Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP) caused by a form of Pneumocystis
carinii, now recognised as a distinct species Pneumocystis jiroveci, in five
homosexual men in Los Angeles. The
disease was originally dubbed GRID, or Gay-Related Immune Deficiency, but
health authorities soon realized that nearly half of the people identified with
the syndrome were not homosexual men. In
1981, the CDC introduced the term AIDS to describe the newly recognised
syndrome, though it was still casually referred to as GRID. In 1983, scientists led by Luc Montaginer at
the Pasteur Institute in France first discovered the virus that causes
AIDS. They called it lymphadenopathy
associated virus (LAV). A year later a
team led by Robert Gallo of the United States confirmed the discovery of the
virus, but they renamed it human T lymphotropic virus type III (HTLV-III). The dual discovery led to considerable
scientific disagreement, and it was not until President Mitterrand of France
and President Reagan of the USA met that the major issues were resolved. In 1986, both the French and the US names for the virus itself were dropped in
favour of the new term, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV).
Global Scenario HIV infection in humans is now
pandemic. As of January 2006, the Joint
United Nations Programmes on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) and the World Health
Organization (WHO) estimate that AIDS has killed more than 25 million people
since it was first recognized on December 1, 1981, making it one of the most destructive
pandemics in recorded history. In 2005
alone, AIDS claimed an estimated 2.4-3.3 million lives, of which more than
570,000 were children. It is estimated
that about 0.6% of the world’s living population is infected with HIV. A third of these deaths are occurring in sub-Saharan
Africa, retarding economic growth and increasing poverty.
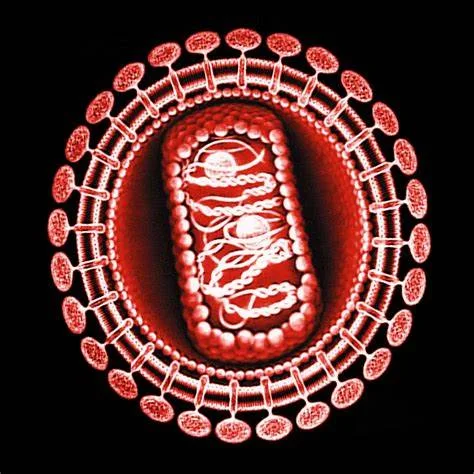
Structure and Genome: HIV is different in structure from
other retroviruses. It is about 120 nm
in diameter which is around 60 times smaller than a red blood cell and roughly
spherical. It is composed of two copies
of positive single stranded RNA that codes for the virus’s nine genes enclosed
by a conical capsid composed of 2,000 copies of the viral protein P24.
RELATED;
1. HIV/AIDS
2. VIROLOGY











No comments:
Post a Comment