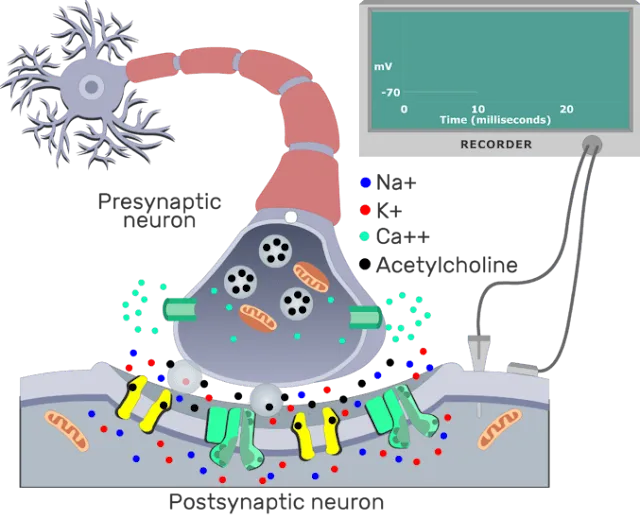
INTRODUCTION: There are several systems of neurotransmitters that are found at various synapses in the nervous system. These groups refer to the chemicals that are the neurotransmitters, and within the groups are specific systems. The first group, which is a neurotransmitter system of its own, is the cholinergic system. It is the system based on acetylcholine. This includes the NeuroMascular Junction (NMJ) as an example of a cholinergic synapse, but cholinergic synapses are found in other parts of the nervous system. They are in the autonomic nervous system, as well as distributed throughout the brain.
THE CHOLINERGIC SYSTEM: The cholinergic system has two types of receptors, the nicotinic receptor is found in the NMJ as well as other synapses. There is also an acetylcholine receptor known as the muscarinic receptor. Both of these receptors are named for drugs that interact with the receptor in addition to acetylcholine. Nicotine will bind to the nicotinic receptor and activate it similar to acetylcholine. Nicotine
Muscarine, a product of certain mushrooms, will bind to the muscarinic receptor. However, nicotine will not bind to the muscarinic receptor and muscarine will not bind to the nicotinic receptor.
AMINO ACIDS AS NEUROTRANSMITTERS: Another group of neurotransmitters are amino acids. This includes glutamate (Glu), GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid, a derivative of glutamate), and glycine (Gly). These amino acids have an amino group and a carboxyl group in their chemical structures. Glutamate is one of the 20 amino acids that are used to make proteins. Each amino acid neurotransmitter would be part of its own system, namely the glutamatergic, GABAergic, and glycinergic systems. They each have their own receptors and do not interact with each other.
Amino acid neurotransmitters are eliminated from the synapse by reuptake. A pump in the cell membrane of the presynaptic element, or sometimes a neighboring glial cell, will clear the amino acid from the synaptic cleft so that it can be recycled, repackaged in vesicles, and released again.
BIOGENIC AMINES AS NEUROTRANSMITTERS: Another class of neurotransmitter is the biogenic amine, a group of neurotransmitters that are enzymatically made from amino acids. They have amino groups in them, but no longer have carboxyl groups and are therefore no longer classified as amino acids. Serotonin is made from tryptophan. It is the basis of the serotonergic system, which has its own specific receptors. Serotonin is transported back into the presynaptic cell for repackaging. Other biogenic amines are made from tyrosine, and include dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine. Dopamine















No comments:
Post a Comment