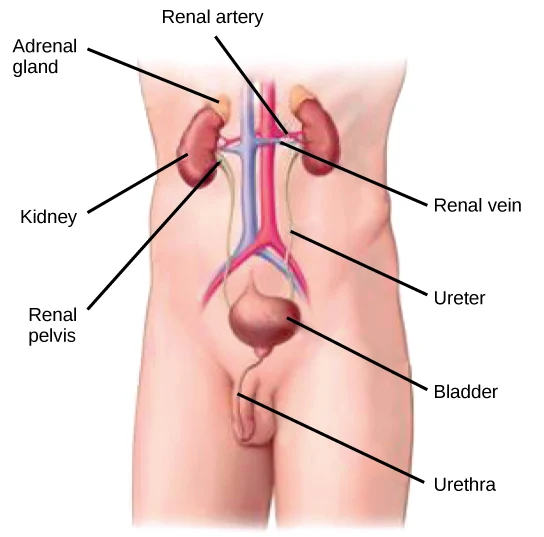
INTRODUCTION: The two kidneys are located in the upper abdominal cavity on either side of the vertebral column, behind the peritoneum. The upper portions of the kidneys rest on the lower surface of the diaphragm and are enclosed and protected by the lower rib cage. The kidneys are embedded in adipose tissue that acts as a cushion and is in turn covered by a fibrous connective tissue membrane called the renal fascia, which helps hold the kidneys in place.
BASIC ANATOMY OF THE KIDNEY: Each kidney has an indentation called the hilus on its medial side. At the hilus, the renal artery enters the kidney, and the renal vein and ureter emerge. The renal artery is a branch of the abdominal aorta, and the renal vein returns blood to the inferior vena cava. The ureter carries urine from the kidney to the urinary bladder.
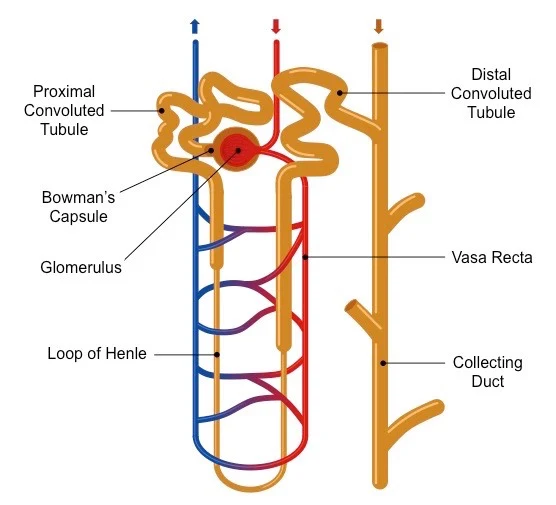
INTERNAL STRUCTURE OF THE KIDNEY: In a coronal or frontal section of the kidney, three areas can be distinguished. The lateral and middle areas are tissue layers, and the medial area at the hilus is a cavity. The outer tissue layer is called the renal cortex; it is made of renal corpuscles and convoluted tubules. These are parts of the nephron and are described in details in our next discussion. The inner tissue layer is the renal medulla, which is made of loops of Henle and collecting tubules which are also, parts of the nephron. The renal medulla consists of wedge-shaped pieces called renal pyramids. The tip of each pyramid is its apex or papilla. The third area is the renal pelvis, and this is not a layer of tissues, but rather a cavity formed by the expansion of the ureter within the kidney at the hilus. Funnel shaped extensions of the renal pelvis, called calyces or in singular: calyx, enclose the papillae of the renal pyramids. Urine flows from the renal pyramids into the calyces, then to the renal pelvis and out into the ureter.
THE NEPHRON: The nephron is the structural and functional unit of the kidney. Each kidney contains approximately 1 million nephrons. It is in the nephrons, with their associated blood vessels, that urine is formed. Each nephron has two major portions: a renal corpuscle and a renal tubule. Each of these major parts has further subdivisions, and we shall discuss more about them later.
RELATED;
3. ALDOSTERONE












No comments:
Post a Comment